Azure Virtual Network
An Azure VNet is an isolated network within the Microsoft Azure cloud. A VNet in Azure provides a range of networking functions similar to the AWS or GCP VPC. These functions include connectivity between virtual machines (VMs), routing, and virtual private networks ( VPNs). A VNet can be broken down into single or multiple subnets. The scope of a virtual network is a single region.
You can create a VNet by performing the following steps:
- Navigate to the Microsoft Azure portal and search forvirtual networks, as shown in Figure 4.9:
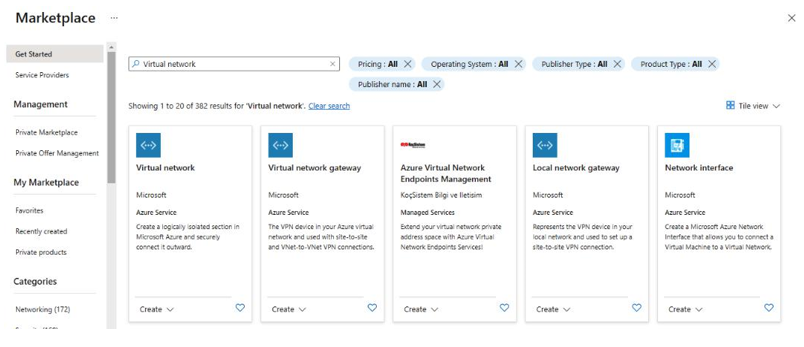
Figure 4.9 – Azure portal
- Next, create the virtual network with the various VNet settings, as shown in Figure 4.10:
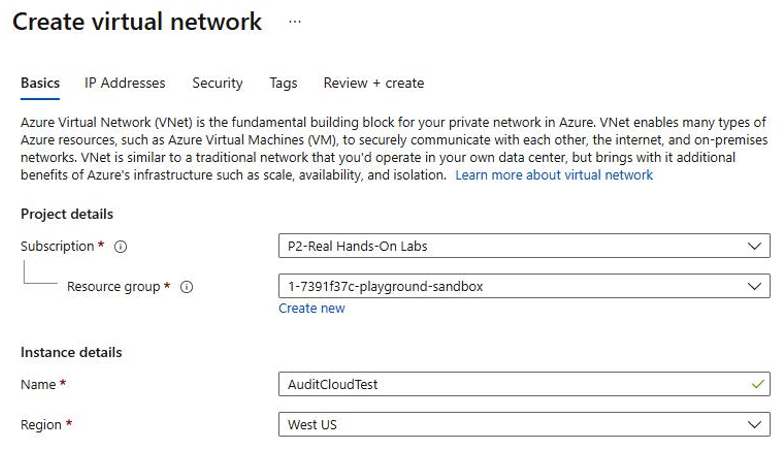
Figure 4.10 – Creating an Azure VNet
- Specify the IP addresses, as shown in Figure 4.11:
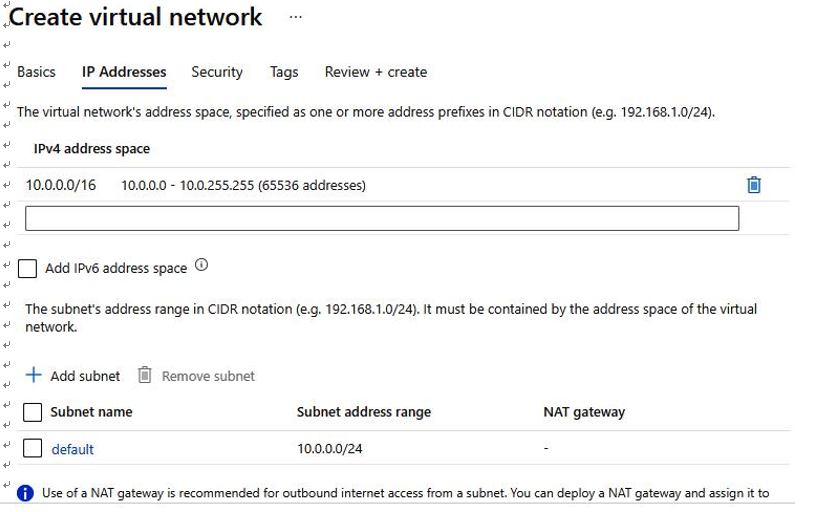
Figure 4.11 – Azure VNet IP address configuration options
- Specify security settings such as DDoS Protection Standard and Firewall, as shown in Figure 4.12:
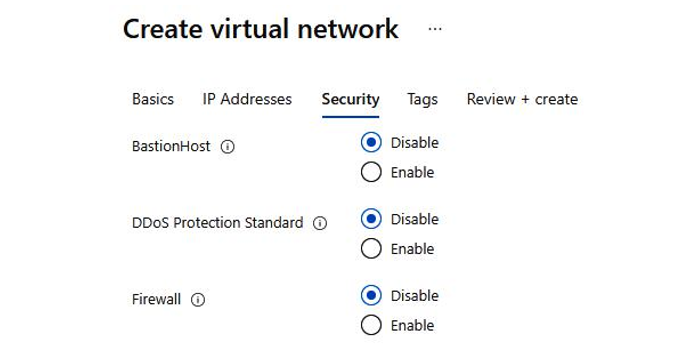
Figure 4.12 – Azure VNet security configuration options
- Lastly, review the configuration and create a virtual network, as shown in Figure 4.13:
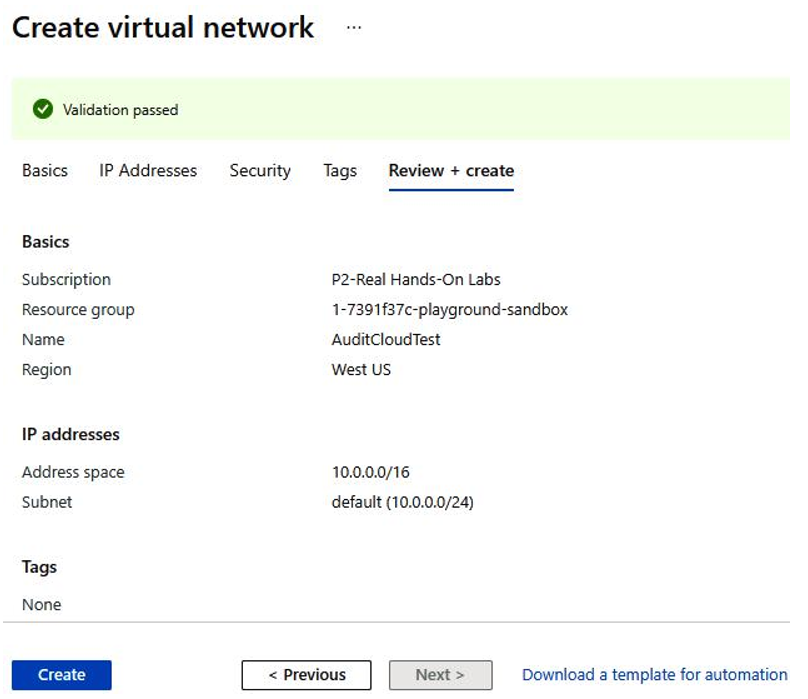
Figure 4.13 – Azure validation of VPC configuration
- With that, virtual network deployment is complete, as shown in Figure 4.14:
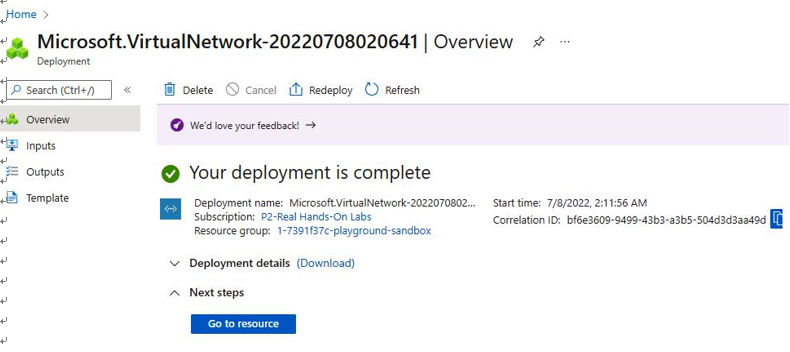
Figure 4.14 – Azure VNet deployed
So far, we’ve reviewed how to build an Azure VNet. We will now look at how to create and configure a GCP VPC.
Google Cloud Platform Virtual Private Cloud
A GCP VPC provides virtual networks very similar to physical networks, except that it is virtualized within the GCP. GCP VPC differs from AWS VPC and Azure VNet as it is not scoped to an individual region. Both AWS VPC and Azure VNet are scoped to an individual region. To create a GCP VPC, perform the following steps:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console and navigate to VPC network, as shown in Figure 4.15:
Figure 4.15 – Google Cloud Console
Review the existing VPCs. Note the existence of several default VPC networks. The IT auditor should take keen note of this as default VPC networks on GCP are inherently insecure. This is shown in Figure 4.16:
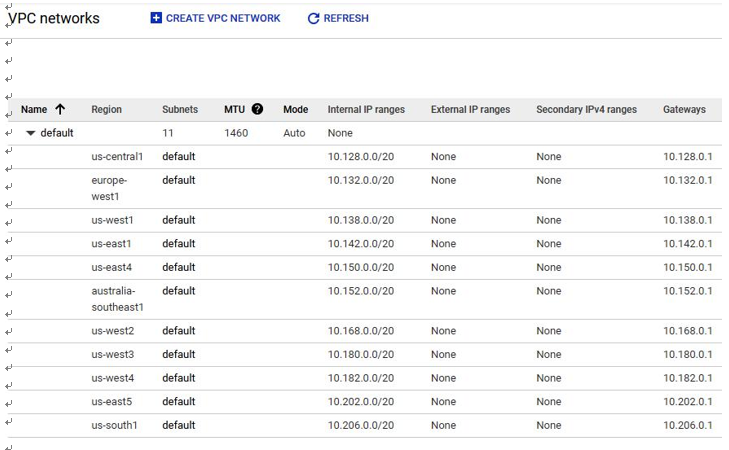
Figure 4.16 – GCP VPC networks
- Next, create a GCP VPC, as shown in Figure 4.17:
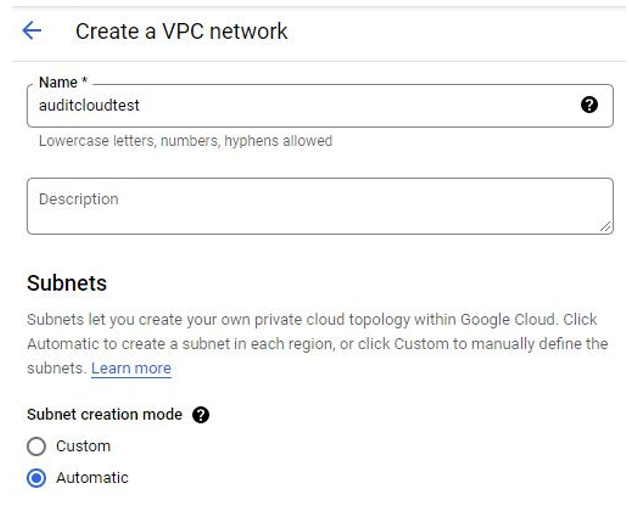
Figure 4.17 – GCP – Create a VPC network
- Specify inbound and outbound firewall rules, as shown in Figure 4.18:
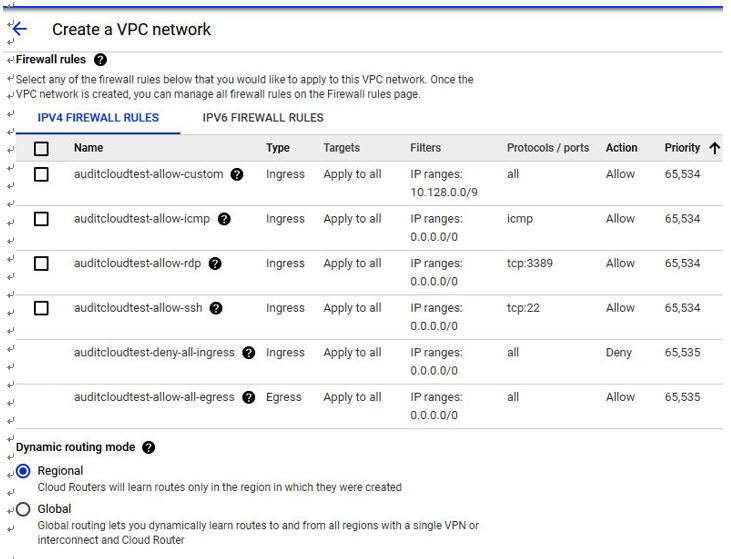
Figure 4.18 – GCP – Firewall rules configuration options
- Next, create the GCP VPC, as shown in Figure 4.19:
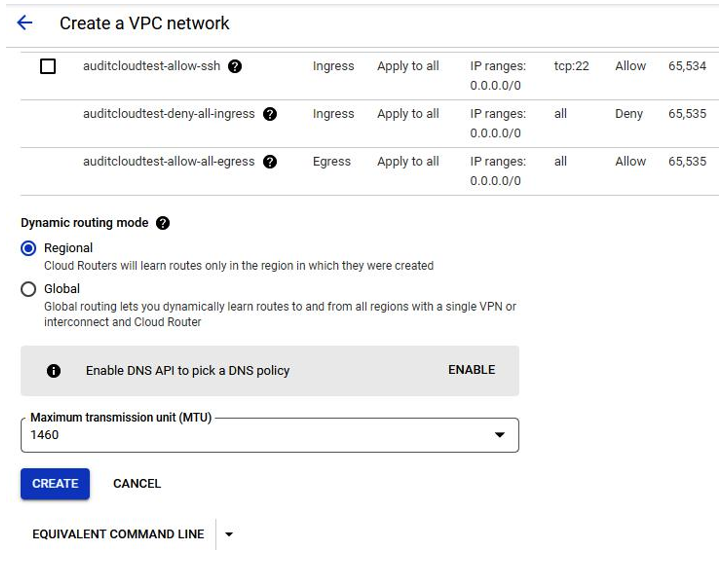
Figure 4.19 – GCP – creating VPC resources
With that, the GCP VPC network has been created, as shown in Figure 4.20:
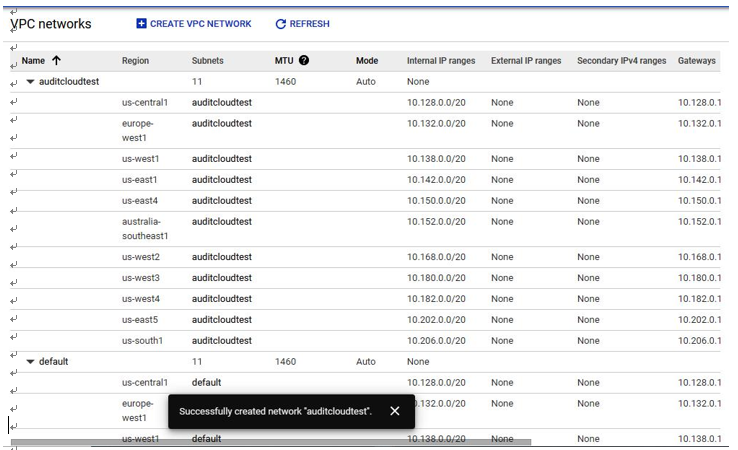
Figure 4.20 – GCP VPC deployed
In this section, we reviewed how to create and configure virtual networks in AWS, Azure, and GCP.
Next, we will look at how to securely configure network controls to protect these networks.


